Medical Blog
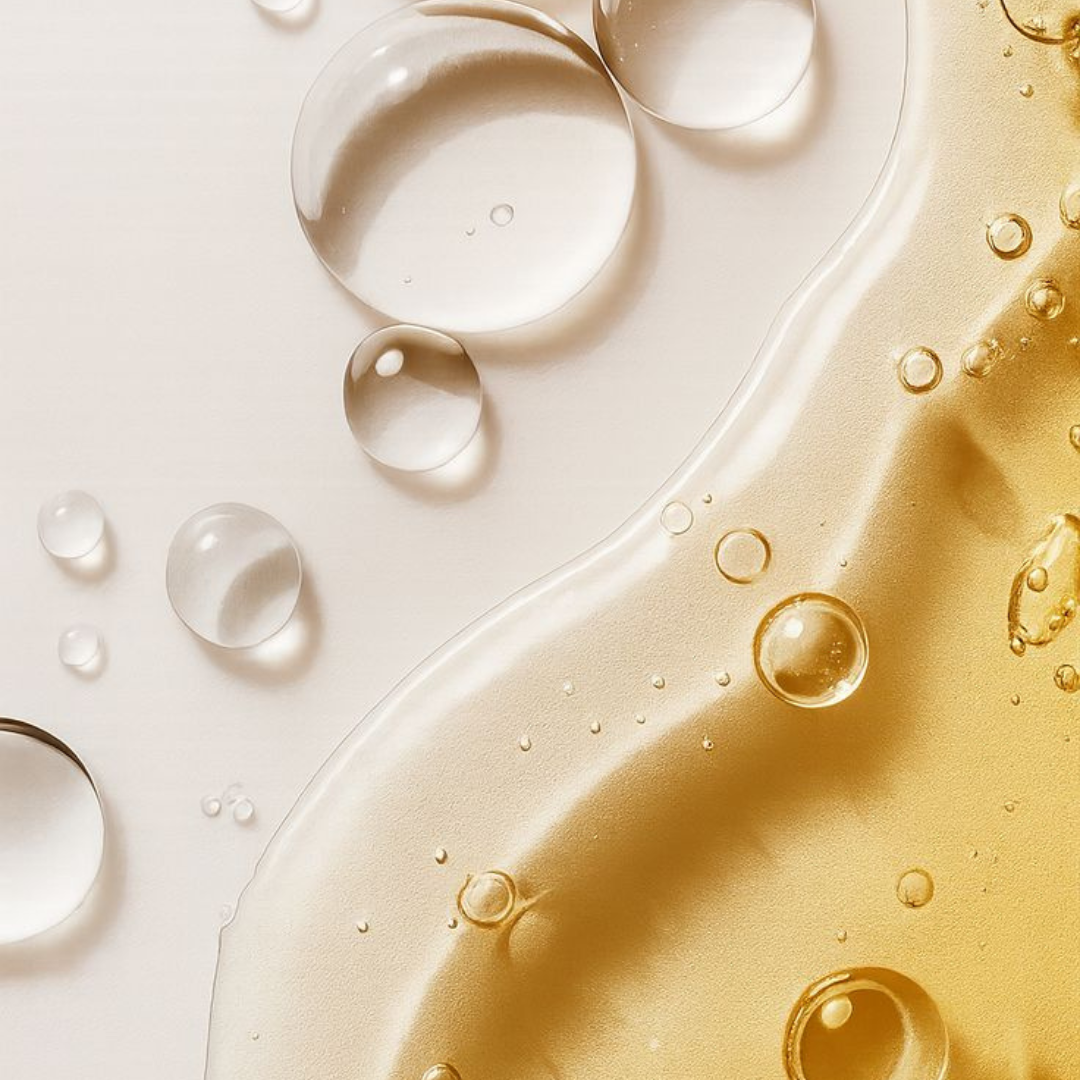

Sculptra vs Skin Boosters: Which Injectable Treatment Is Best for You?
Curious about the difference between Sculptra and skin boosters? While both treatments rejuvenate and refresh the skin, they work in completely different ways. Sculptra gradually restores lost volume and firmness by stimulating collagen, while skin boosters deeply hydrate for smoother, more radiant skin. Discover which injectable is right for your skin goals this summer.

How to Slow Skin Aging This Summer: The Key Factor You Can Control
Not all ageing is created equal.
Intrinsic ageing happens naturally with time, but extrinsic aging — driven by UV exposure and environmental stress — is largely preventable. Studies show that daily use of broad-spectrum SPF can visibly improve skin clarity and texture in as little as 12 weeks. As summer approaches, protecting your skin from photoaging is one of the most effective ways to slow the signs of ageing and maintain a youthful, healthy glow.
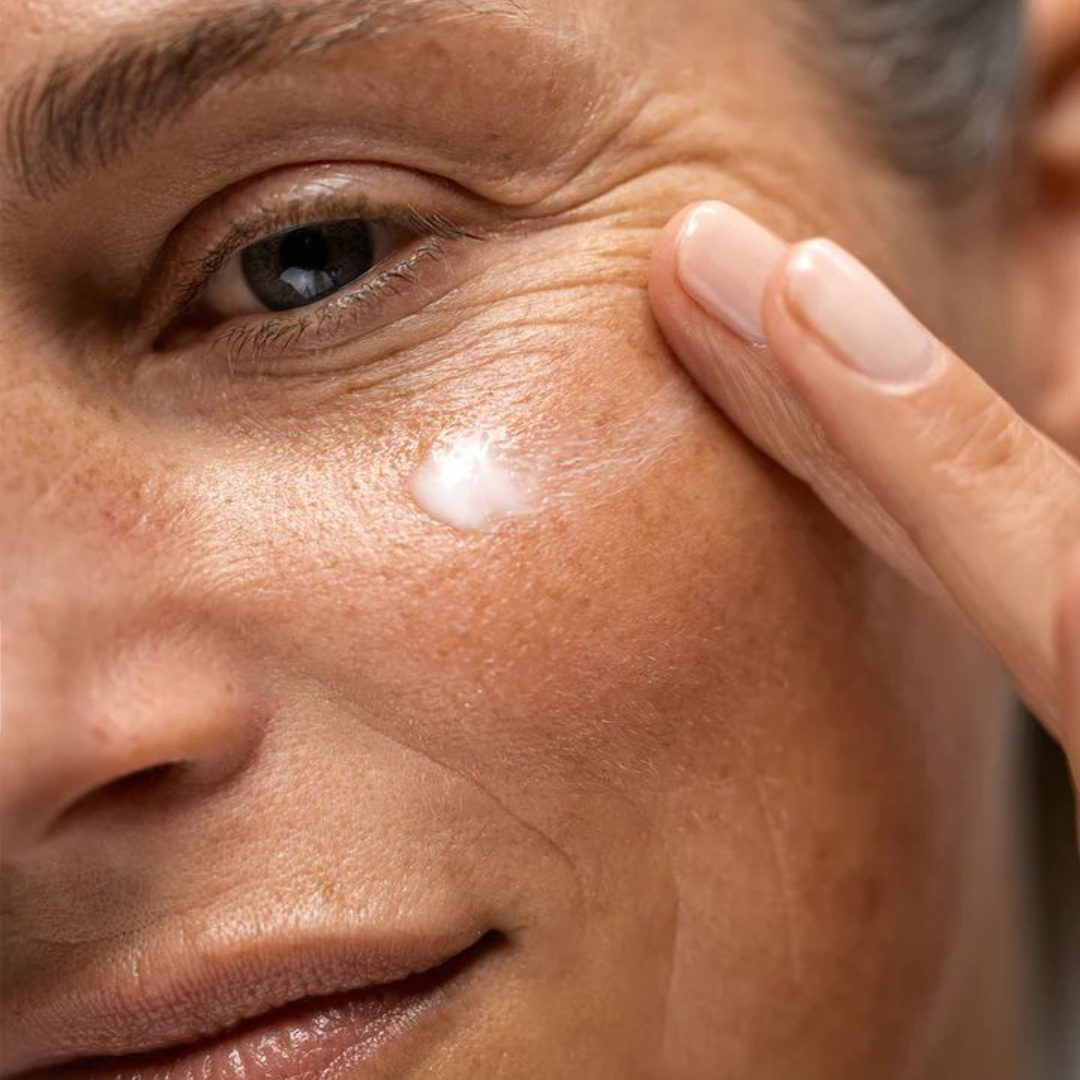
How to Build a Long-Term Aesthetic Plan (Instead of Chasing Quick Fixes)
In today’s fast-paced, filter-fuelled world, it’s tempting to chase the latest ‘miracle’ treatment promising instant results. But real, long-lasting beauty isn’t built overnight — it’s the result of consistency, strategy, and understanding your skin’s long-term needs. Quick fixes might offer a fast glow-up, but they often fade just as quickly. A long-term aesthetic plan empowers you to invest in your skin’s health, strength, and longevity.
Skin Blog

Sun, Salt & SPF: The Real Secrets to Summer-Proofing Your Skin
As the sun heats up, your skin needs extra care. From antioxidant protection and Vitamin A to hydration and summer-safe treatments, these expert tips will help you maintain healthy, glowing skin all season long.

Summer Skincare Tips: Expert Advice to Protect and Rejuvenate Your Skin
Summer Skincare Essentials
Sun, sweat, and sand — summer can be tough on your skin. The good news? With the right essentials, you can protect, prevent, and repair. From daily SPF and antioxidant-rich serums to Vitamin A and gentle cleansing, these skincare staples keep your skin healthy, hydrated, and glowing all season long.
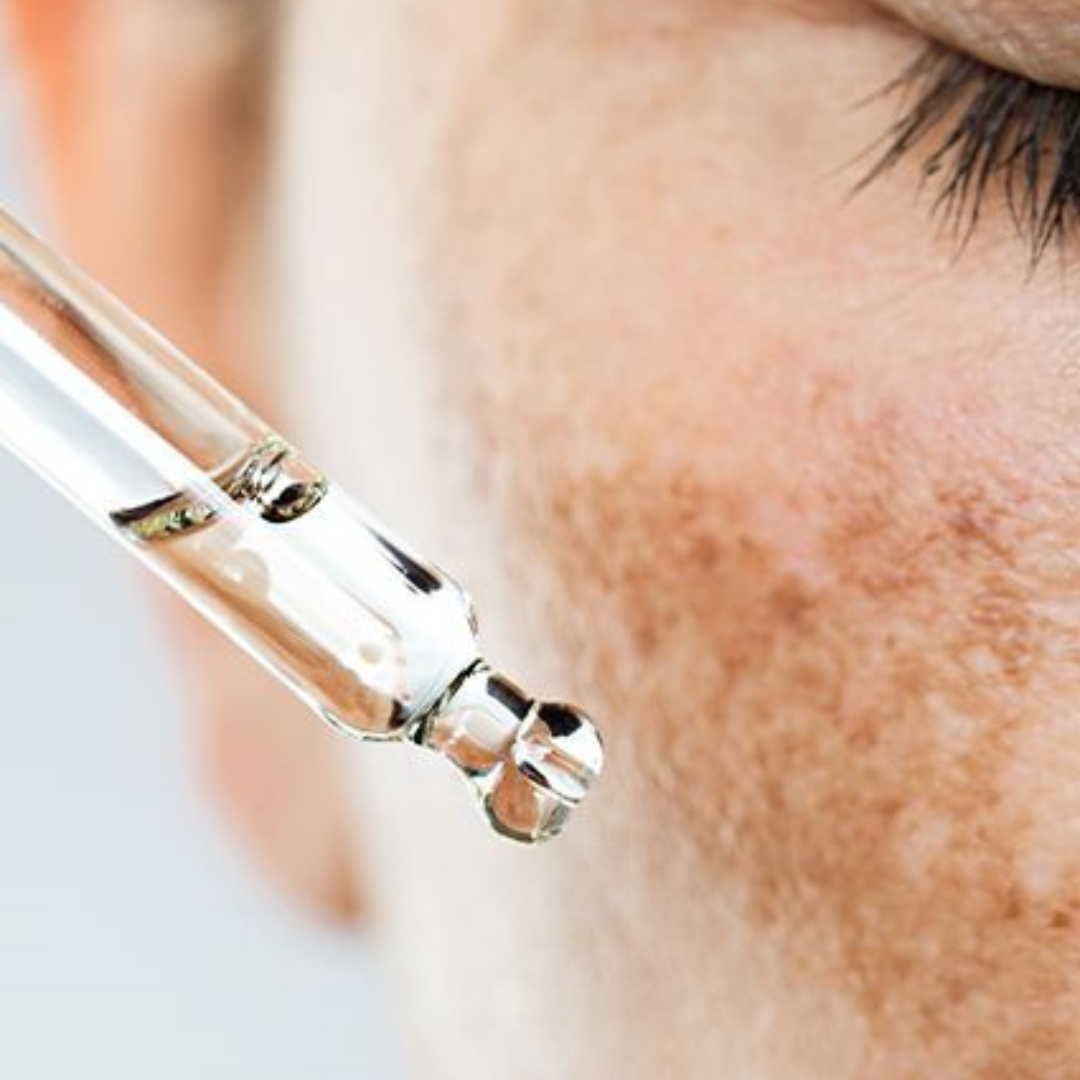
4 Things Your Skin Therapist Wants You to Know About Melasma
Melasma isn’t just “a bit of pigmentation” — it’s complex, persistent, and often frustrating. Unlike standard sunspots, melasma is driven by heat, hormones, and inflammation, making it one of the trickiest skin conditions to manage. In our latest blog, we break down what really works (and what to avoid), from the right ingredient combinations to why heat-based treatments can make things worse.
Discover the smarter, gentler way to get melasma under control — and why your skin can still glow, melasma or not.
TFP Academy Blog
Breaking Free from Brand-Led Training in Aesthetic Medicine
Most cosmetic injectors begin their education with pharmaceutical company workshops — but these sessions often prioritise product promotion over true clinical learning. At The Face Place Academy, we take a different approach. Our workshops are small, hands-on, and brand-neutral, giving you the skills, confidence, and versatility to treat patients safely and effectively with a wide range of products and techniques.

Your Future in Cosmetic Medicine Starts Here
Thinking about a career in cosmetic medicine? Whether you're a registered health professional curious about injectables or ready to make a full career pivot, The Face Place Academy offers the training and support to get you started. Our comprehensive, hands-on courses blend science, artistry, and ethics—helping you build the confidence and skills to thrive as a cosmetic injector, no matter your experience level.

From Hesitation to Confidence: A Trainer’s Insight into Mastering the Foundation of Neuromodulators
Around The Clinic

Sustainability in Action: How Our Clinic is Making a Real Difference
Dr Jenni's Updates

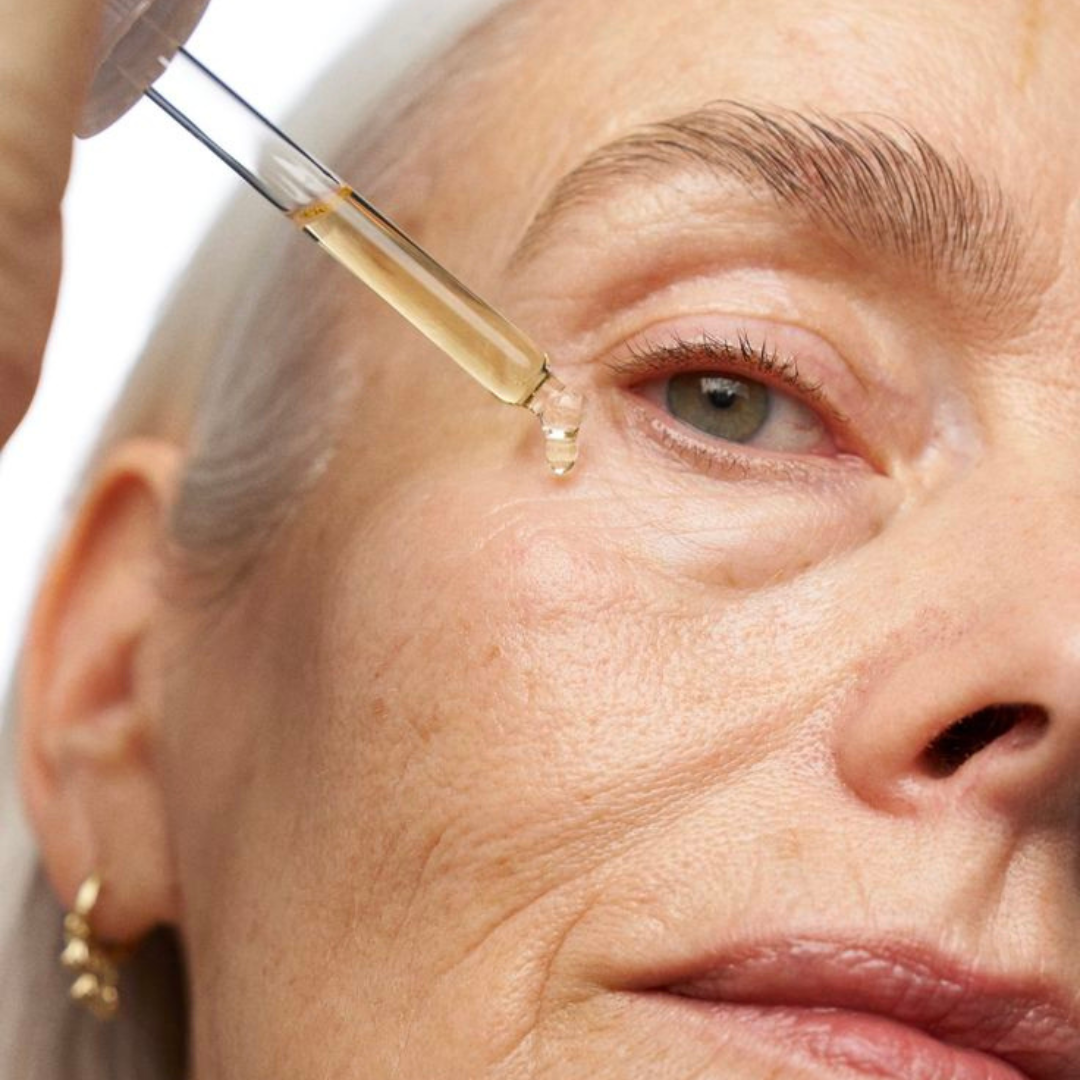
Reflections on My Journey and Expanding Treatment Offerings at The Face Place
As I step into my third month as owner, I’m excited to expand our offerings with evidence-based treatments that deliver natural, lasting results. This month we welcome Sculptra — a collagen-stimulating injectable that restores firmness and skin quality, supporting healthy ageing and confidence at every stage.
— Dr Jenni Irvine

Coming Home: My First Month as Medical Director at The Face Place
It’s hard to believe it’s already been a month since I returned to The Face Place. Stepping back into the clinic has felt like coming home — reconnecting with familiar faces, meeting new team members, and settling into an environment that embodies integrity, ethics, and excellence. I’m excited to build on the legacy Cat has created while getting to know our wonderful patients and shaping the next chapter together.

Dr Cat's August Update
After 25 incredible years, The Face Place enters a new chapter. On 31 July, Dr Jenni Irvine officially took over ownership—bringing with her a deep understanding of our values, culture, and commitment to excellence. While the heart of The Face Place remains the same, this transition marks an exciting new era for the team, our patients, and what’s to come. In this heartfelt farewell, Dr Cat reflects on the journey so far, the decision to pass the torch, and what’s next in her own inspiring story.
